
Symptoms and Causes

Thrush
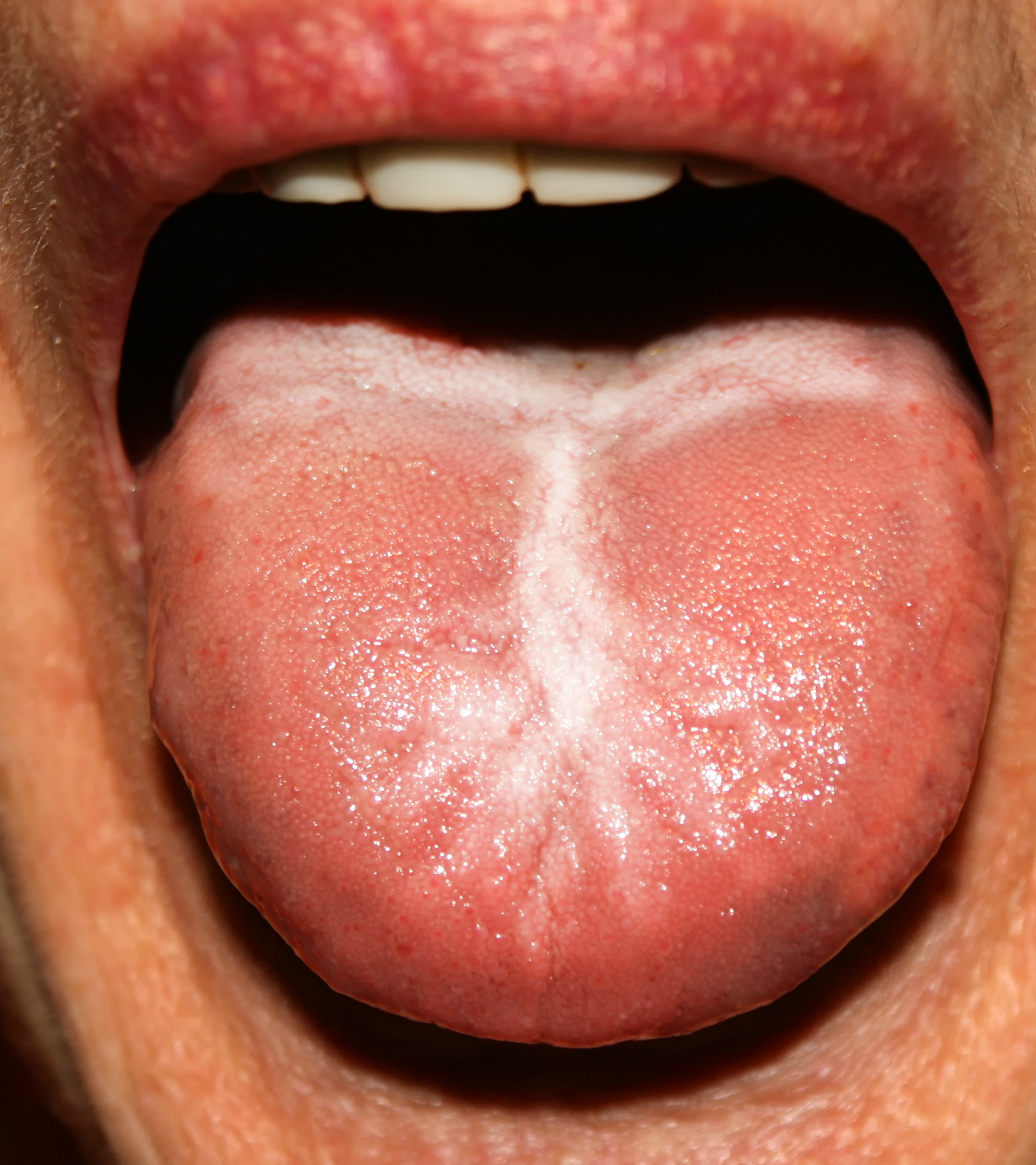
Thrush is a fungal infection that leaves white patches and spots on the tongue and inside the mouth. It itches and can be painful, but can be treated with an anti-fungal medication prescribed by your doctor.
Hairy Tongue

Hairy tongue occurs when filiform papillae form on the tongue. These millimeter-long cone-shaped bacteria look like hair and are the result of bacteria growth in the mouth due to smoking or poor oral hygiene habits.
Black Tongue
Like hairy tongue, black tongue is caused by bacteria growth often due to poor oral hygiene, an all-liquid diet, low saliva production or side effects from medications. It can be treated with simply brushing the tongue (and your teeth). But ask a doctor if you suspect a medication you are taking (such as antibiotics) is the cause.
Kawasaki Disease

A bright red tongue, especially one that looks like a strawberry, could be the sign of Kawasaki disease, a rare illness that inflames blood vessels. It could also be a symptom of scarlet fever. If the tongue is red, smooth and causing you pain, it might be that you're not getting enough vitamin B3 (such as niacin).
Nerve Damage
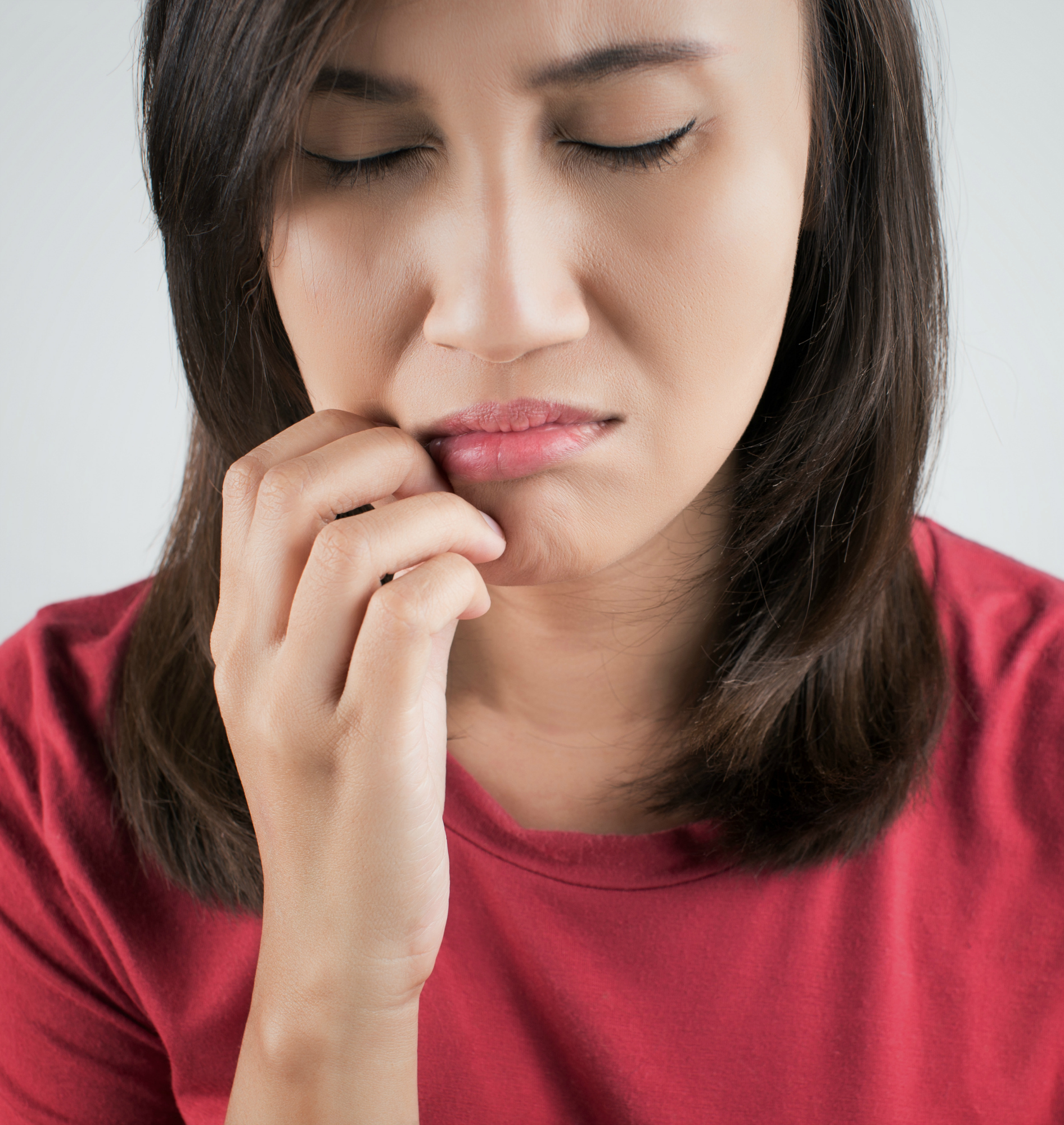

If your tongue has a burning sensation but you haven't just eaten a spicy meal — and if the burning is prolonged — this could be a sign of nerve damage or disorder in the tongue. Other causes could be dry mouth, infections, acid reflux or diabetes.
Vitamin Deficiency
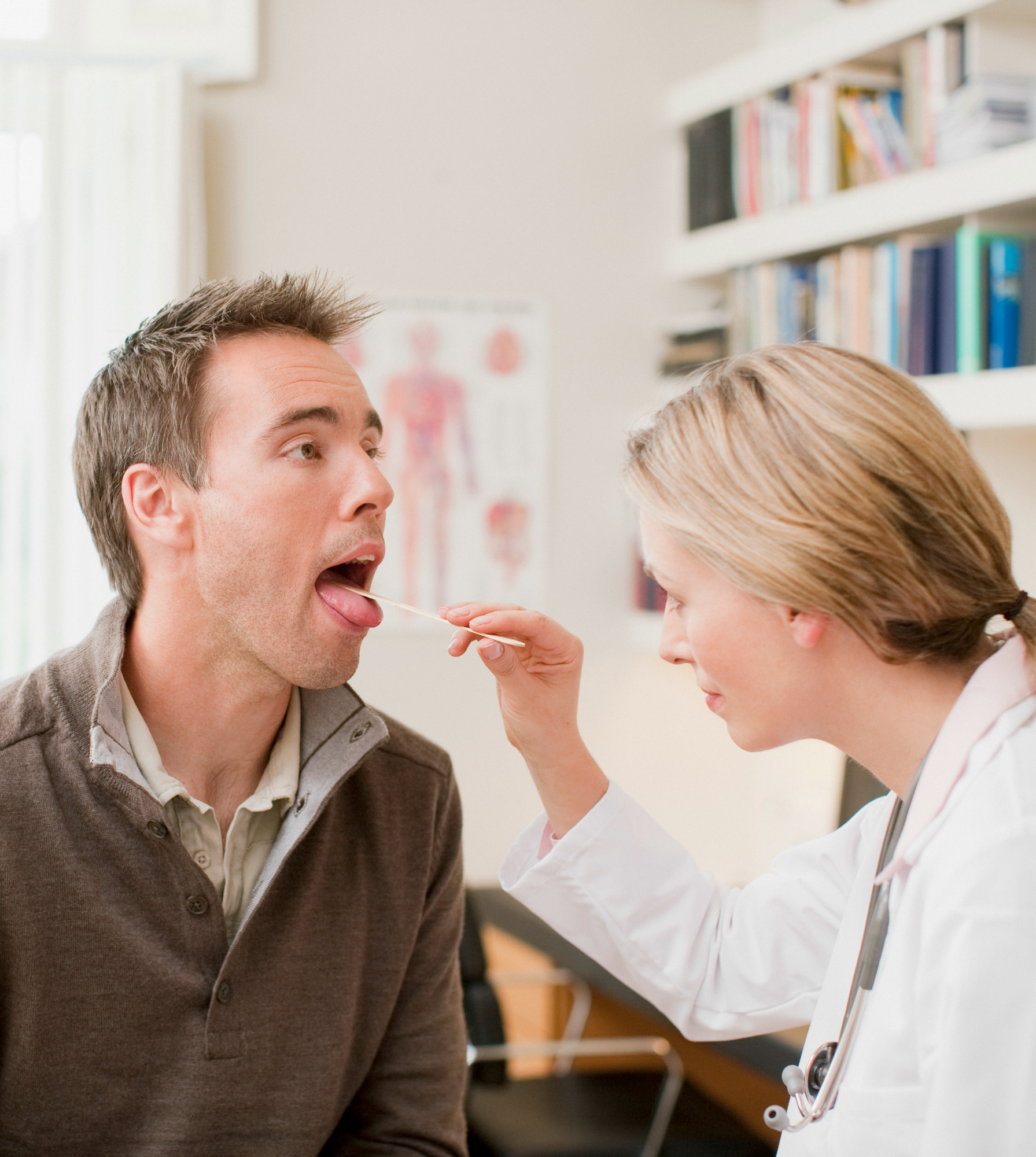

If the surface of your tongue is abnormally smooth, that could be a sign of certain vitamin deficiencies, including a lack of iron, folate or vitamin B12. If you wear dentures, they might be the culprit.
Bumps and Canker Sores
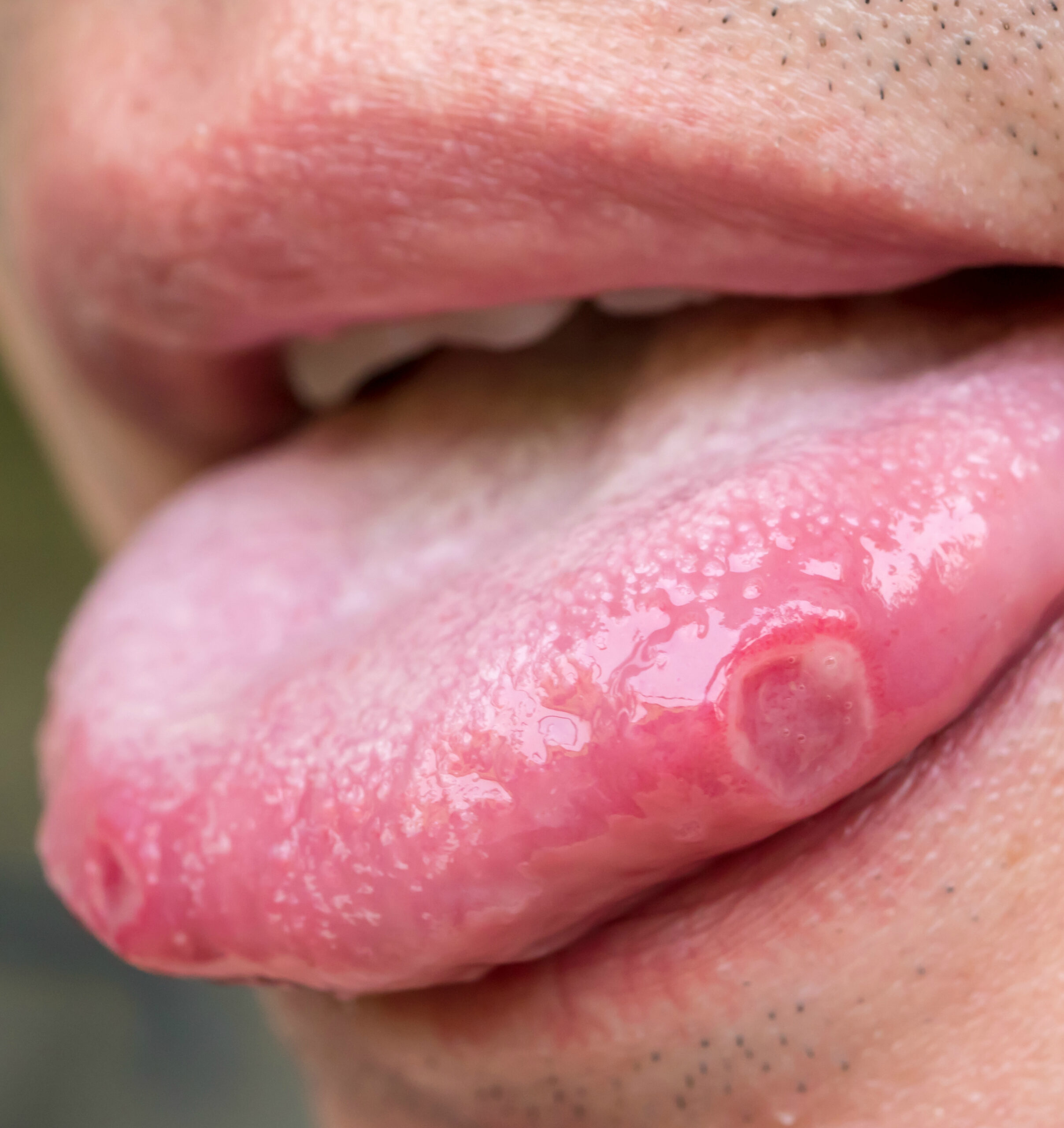
Almost everyone has had a canker sore at least once in their life. They're common and occur when the tongue gets irritated by braces, scratchy food or lack of brushing and flossing. Canker sores should clear up within a couple of days. If they don't, check with your doctor to make sure they're not cancerous.
Infection

Tongue soreness should typically clear up within a day or two. If not, it's important to see your dentist or doctor. A sore tongue can be the result of iron deficiencies, an infection, a virus or other more serious problems, such as cancer.
Macroglossia
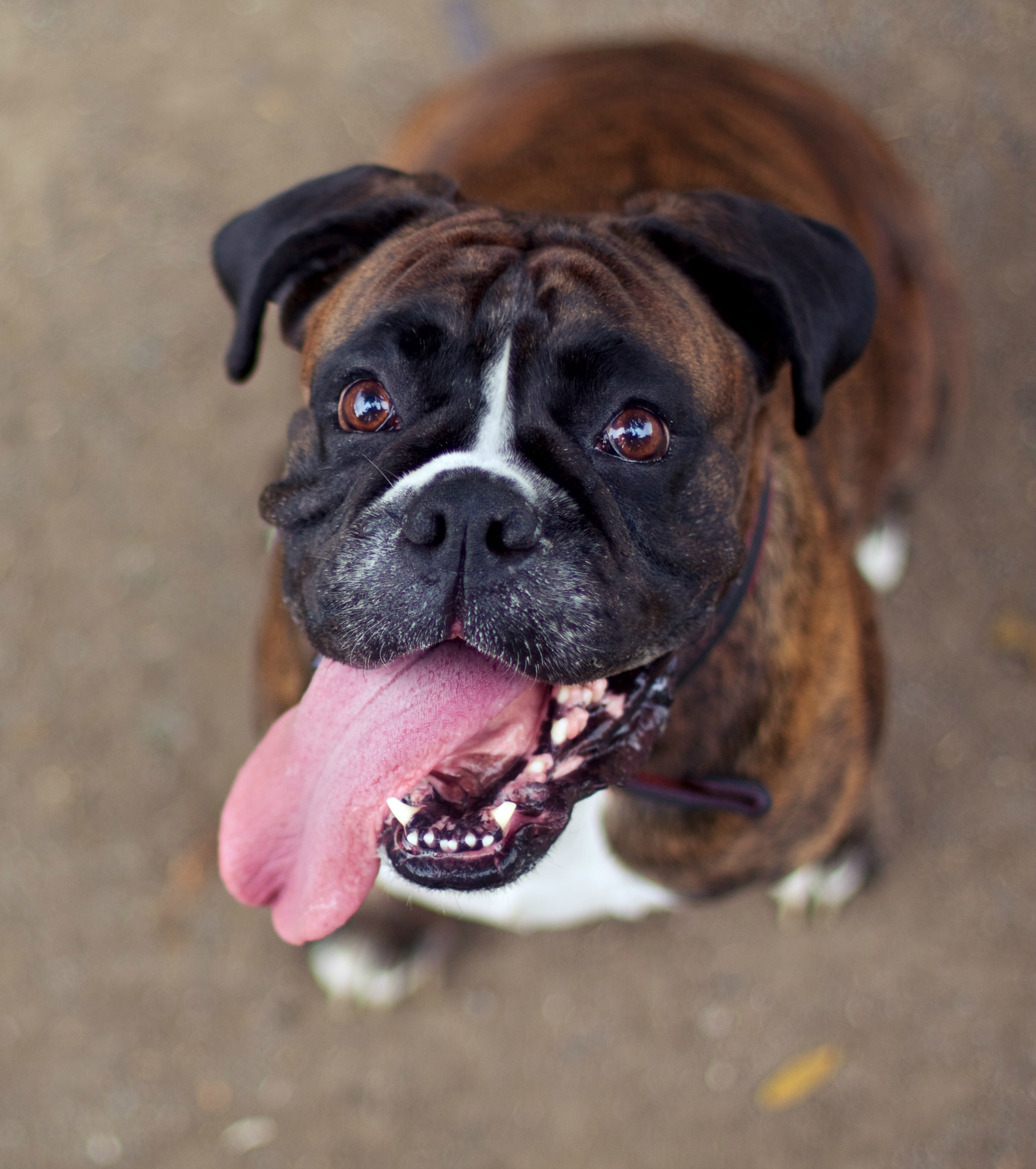

Macroglossia is when the tongue is abnormally large. There are a number of causes, including congenital issues such as Down syndrome. For an enlarged tongue not from birth, the cause for enlargement can be serious, such as the result of trauma, tumors or another type of growth.
Fissured Tongue
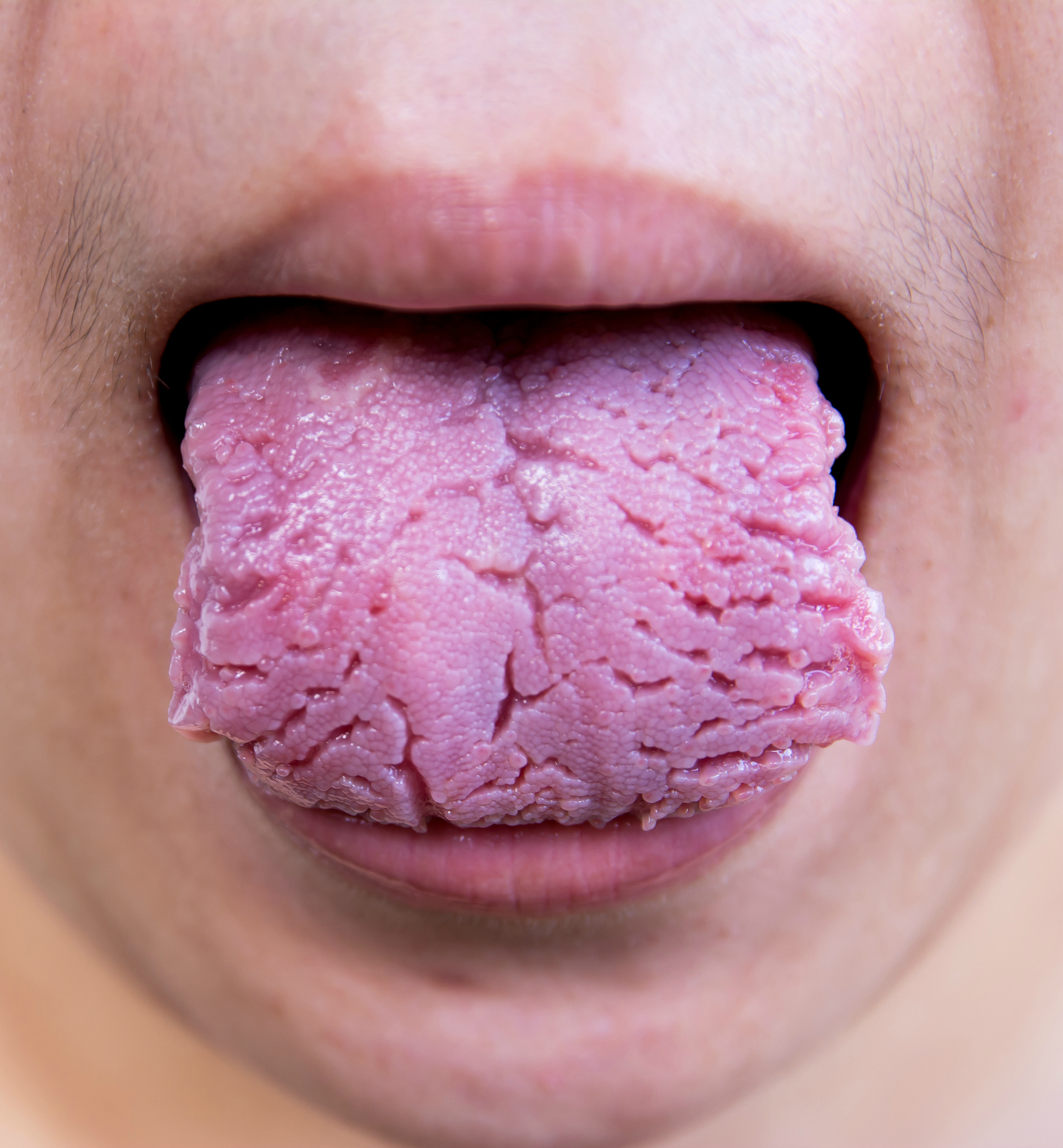
Fissured tongues are a normal kind of tongue, and people who have them were born with them. The concern with fissured tongues is that food and bacteria can get caught in the deeper grooves. Brushing twice daily and flossing at least once per day is important. Those with a fissured tongue might also consider a tongue scraper or rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash.
HPV
Human papillomavirus is a sexually transmitted disease. Some strains of it dramatically increase your risk of getting cancer, either of the cervix or in your mouth. Symptoms of oropharyngeal cancer, which is caused by HPV, can include sore throats that don't go away, earaches, swollen lymph nodes, pain when swallowing and unexplained weight loss.
Tongue Cancer

Tongue cancer is serious and its symptoms include pain, a change in your voice or trouble swallowing. There are several common causes of tongue cancer, including human papillomavirus, a common sexually transmitted infection. Certain strains of HPV increase your risk of developing cancer. Also increasing your risk of tongue cancer are smoking, drinking and not taking care of your teeth and gums.
Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease
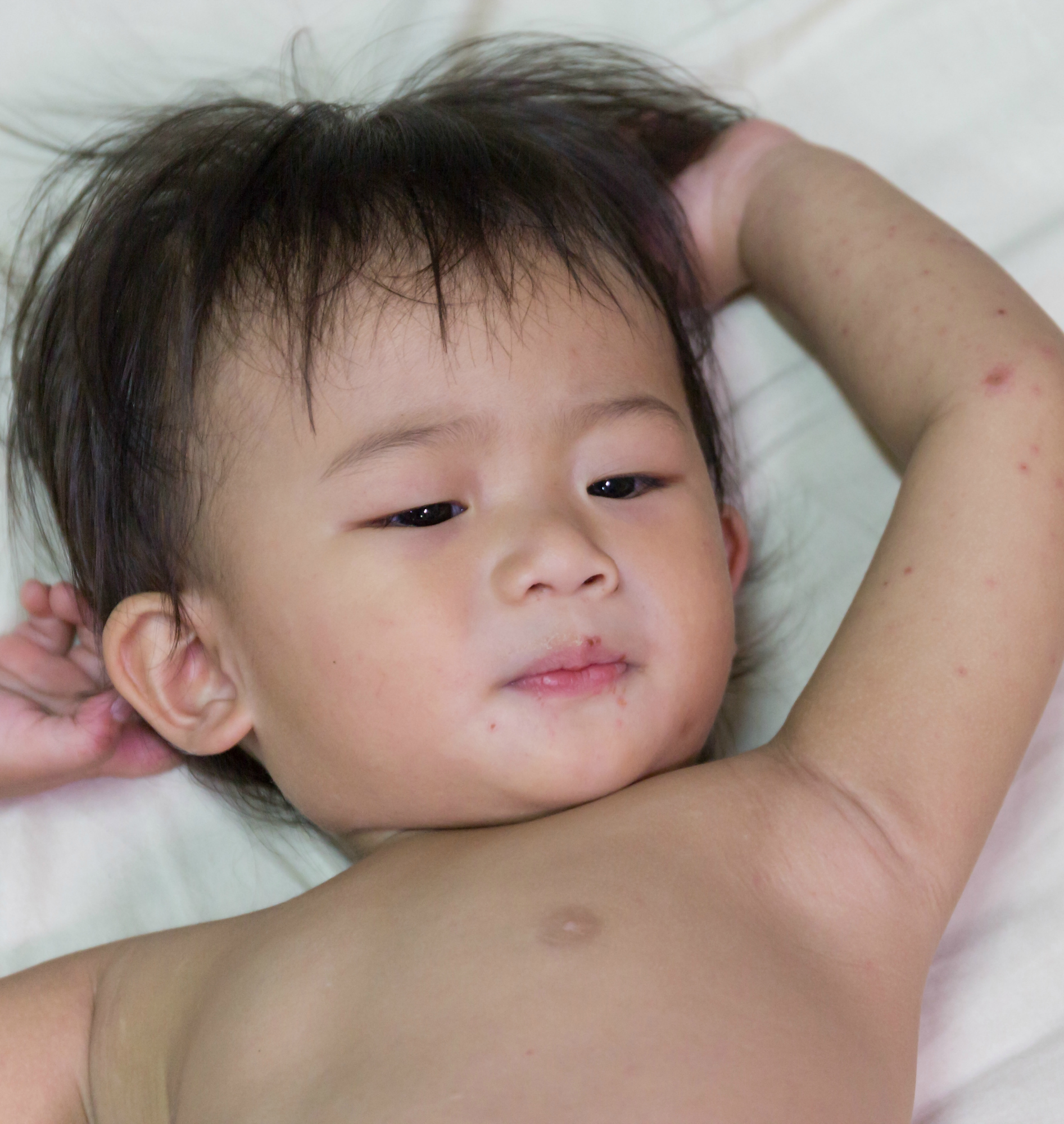
A very common and highly contagious childhood infection is hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Painful sores develop on the tongue and inside the mouth, as well as on the hands and feet. There's no specific treatment, other than rest and time.
Hormonal Changes

Hormones affect everything, including the tongue. Menstruation, menopause and hormone fluctuations due to aging can all show up on the tongue. Around a woman's period, the increased progesterone might result in canker sores. During menopause, women may experience dry mouth, altered taste, gum disease or difficulty swallowing — all due to a decrease in saliva production.
Allergies

People who suffer from allergies, either airborne or food-based, might experience their reactions right on the tongue. People with hay fever frequently feel a tingling on the tongue. Those who have eaten something they're allergic to might feel itchiness or slight swelling on their tongue.
Neuralgia

Severe pain in the back of the tongue is a common symptom of neuralgia, a malfunction of an important cranial nerve. The pain is typically brief occurs intermittently. The cause isn't well-known but might be due to an artery pressing on the nerve.
Oral Lichen Planus
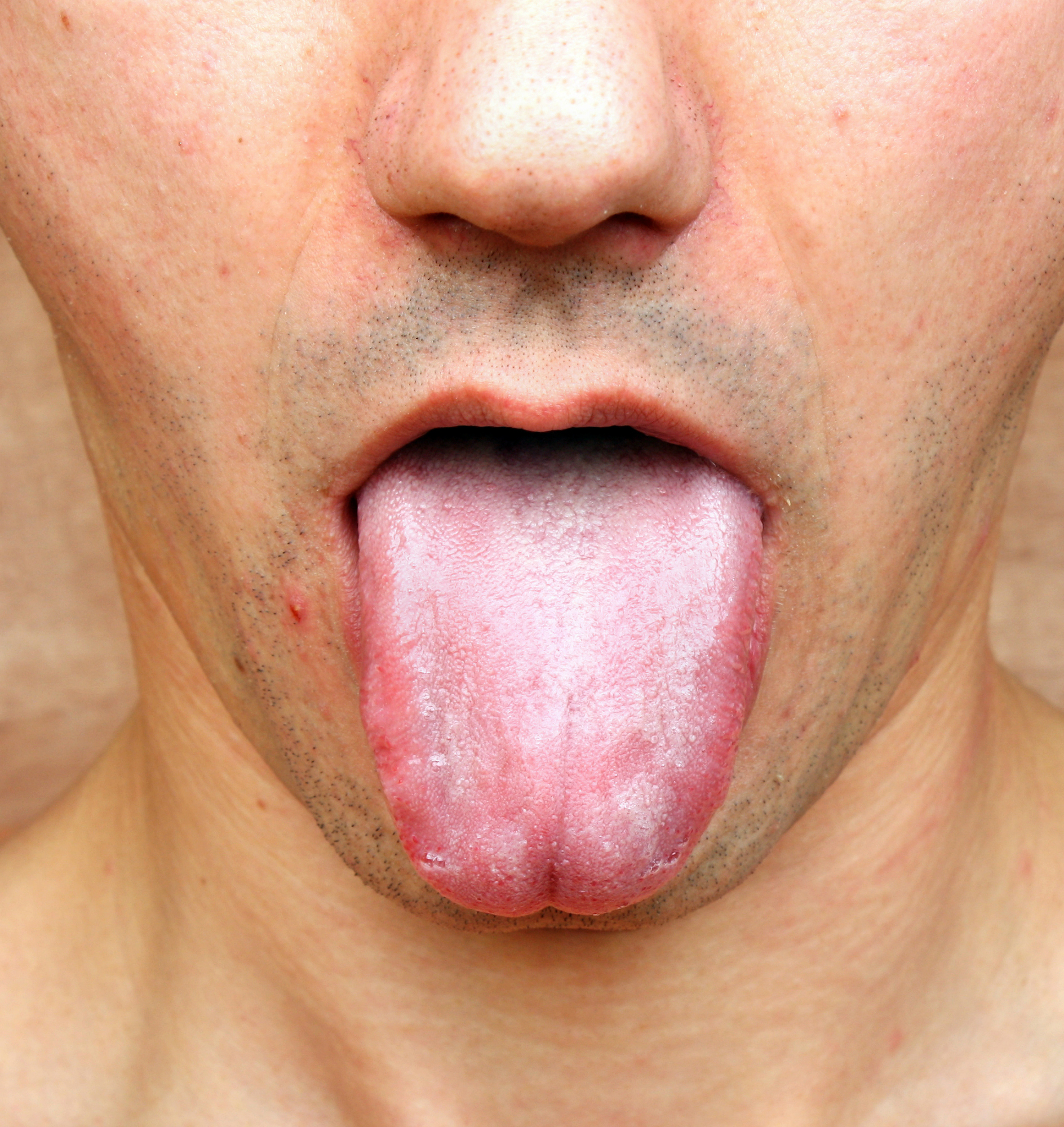
Oral lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that causes mucous inside the mouth to separate into a lace-like pattern on the cheeks and tongue. It's not contagious. It's caused by an autoimmune disorder. Those who have lichen planus may experience pain or discomfort, or bleeding and irritation while brushing their teeth.




